Security/Reviews/CloudServices/Marketplace Payments
Contents
- 1 Status
- 2 Team
- 3 Open issues/risks
- 4 Stage 1: Definition
- 5 Stage 2: Design
- 6 Stage 3: Planning
- 7 Stage 4: Development
- 8 Stage 5: Release
- 9 Stage 6: Post Implementation Review
- 10 Team status notes
Status
| Identity (TEMPLATE) | |
|---|---|
| Tracker Bug | - |
| Stage | Definition |
| Status | Green (Green, Yellow, Red?) |
| Release Target | |
| Health | - |
| Status Note | - |
Team
| Product manager / Feature manager | Lindsay Saunders, Stephanie Turner and Caitlin Galimidi. |
| Engineering lead | |
| Engineering manager | Payments - Andy McKay
Marketplace - |
| Security lead | Adam Muntner |
| Privacy lead | |
| Localization lead | Peiying Mo |
| Accessibility lead | - |
| QA lead | Krupa Raj |
| UX lead | Elizabeth Hunt |
| Product marketing lead | |
| Additional members | Amy Tsay - Community
Scott DeVaney - Editorial Manager |
Open issues/risks
Stage 1: Definition
Introduction
Payments tied to Firefox Accounts as a reusable service with all Mozilla properties
Project Links
- Payments team home - https://wiki.mozilla.org/CloudServices/Payments
- Payments tied to FxA project wiki page - https://wiki.mozilla.org/CloudServices/Payments/FirefoxAccounts
- In App Payments - https://wiki.mozilla.org/Marketplace/InAppPayments
Project Links - Mana pages (Mozilla staff/contrib LDAP account needed)
- Addons/Marketplace - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=9601080
- Payments - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/display/MARKET/Payments
- Payments Production Support - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/display/MARKET/Payments+Support
- Processing refunds - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/display/MARKET/Processing+refunds
- Spartacus / Webpay physical network architecture (search page for "Spartacus") - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/display/NOC/VLAN+assignments
- Marketplace / AMO physical infrastructure - https://mana.mozilla.org/wiki/display/SVCOPS/Marketplace+AMO
Project Links - Receipt Verification
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/Marketplace/Monetization
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/Marketplace/Monetization/Validating_a_receipt
- https://github.com/mozilla/receiptverifier
- https://inapp-pay-test.paas.allizom.org/
API Docs
- http://firefox-marketplace-api.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/payment.html#in-app-products
- http://firefox-marketplace-api.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/payment.html#preparing-payment
- http://firefox-marketplace-api.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/payment.html#payment-status
- WebPayment API (navigator.Mozpay) - https://wiki.mozilla.org/WebAPI/WebPayment
- Web Payments Provider - https://wiki.mozilla.org/WebAPI/WebPaymentProvider
Related
- Firefox Accounts Payments Proposal - https://wiki.mozilla.org/CloudServices/Payments/FirefoxAccounts
- Jugband engineering metrics and activity for Marketplace - https://jugband.paas.allizom.org/
Historical examples of app payment fraud
- How to detect and prevent in-app payment fraud - http://blog.soom.la/2013/09/how-to-detect-and-prevent-in-app.html
- Apple/Google FTC & EU billing scrutiny - http://yottafire.com/2014/07/apple-is-showing-resentment-with-limit-in-in-app-purchases/
- Kids and in-app purchases, FTC, EU - http://finance.yahoo.com/news/amazon-ready-fight-ftc-app-181013610.html
Use Cases
Webpay is an implementation of the WebPaymentProvider spec. It hosts the payment flow inside navigator.mozPay() when making app purchases or in-app payments on Firefox OS.
- Webpay provides a REST API for clients to interact with the server.
- All API’s use JSON for request and responses.
Data Flows
Diagrams
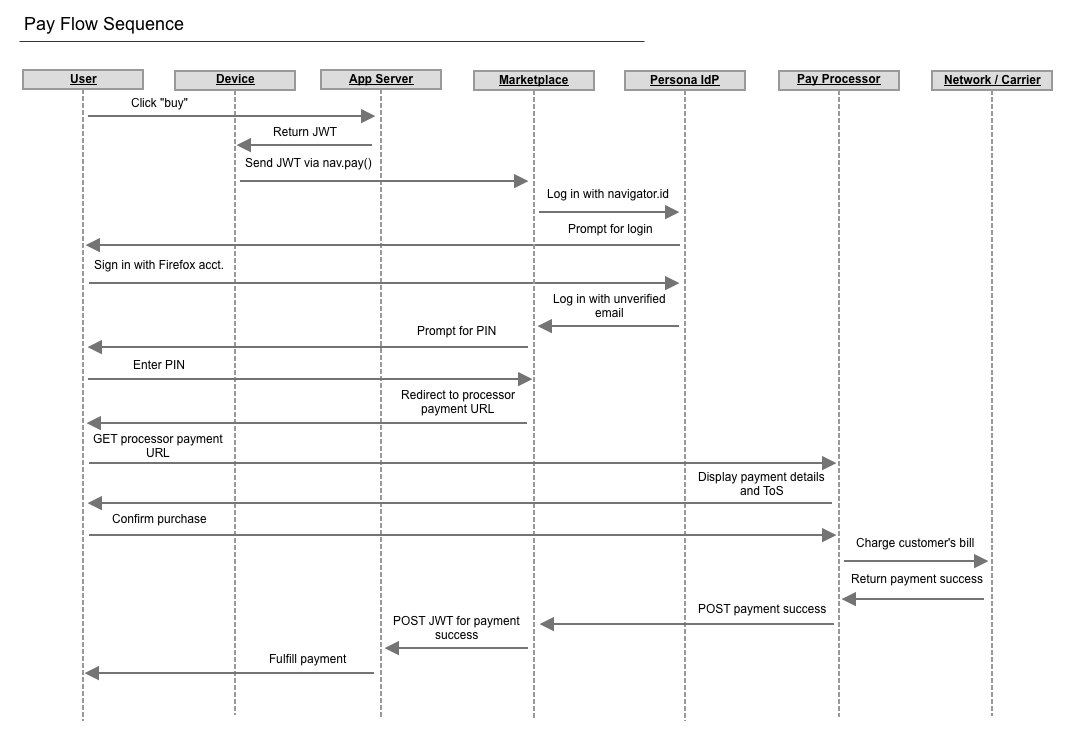
Payments Flow Sequence
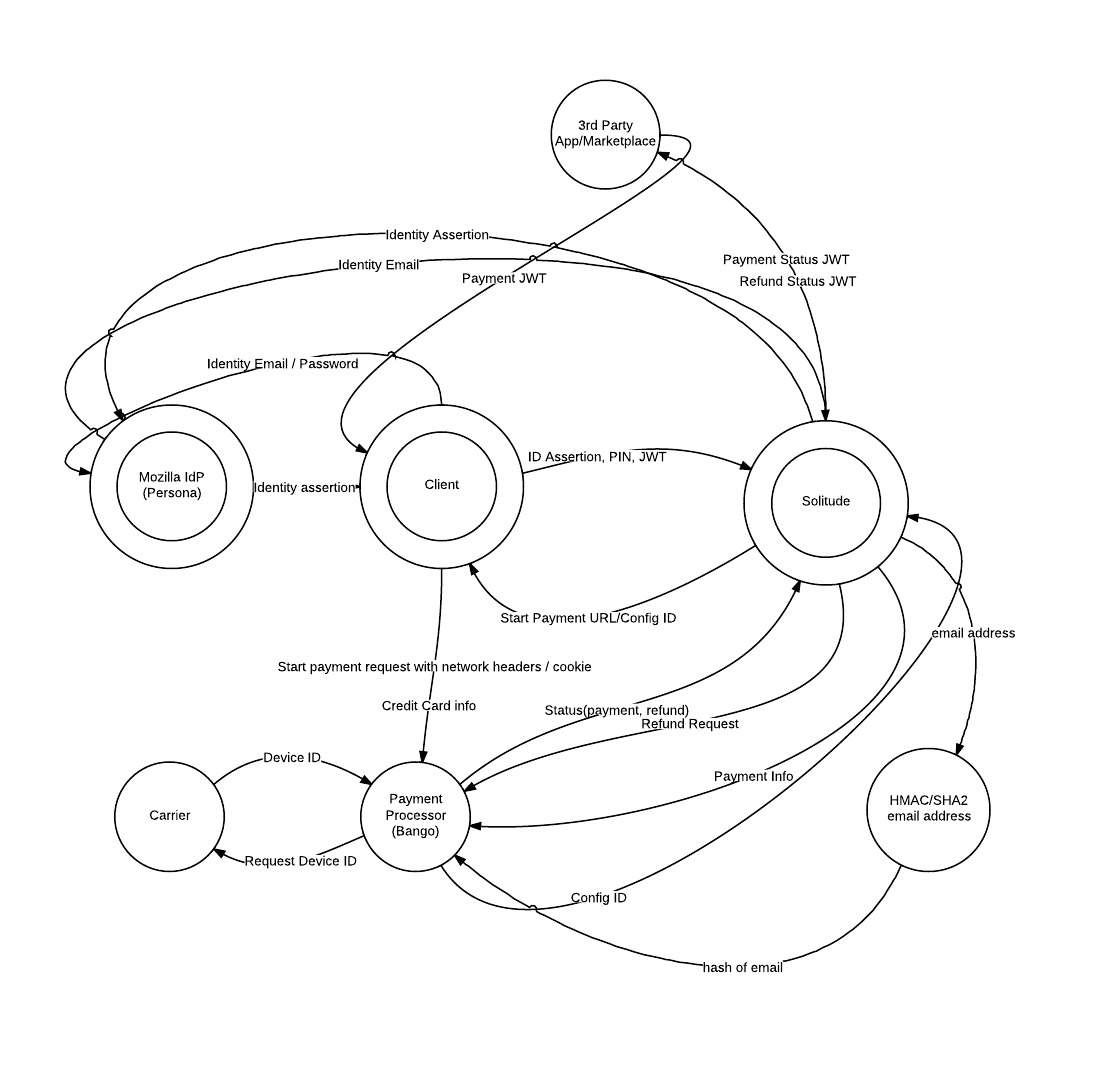
Payments Data Flow Diagram
Pin Flow
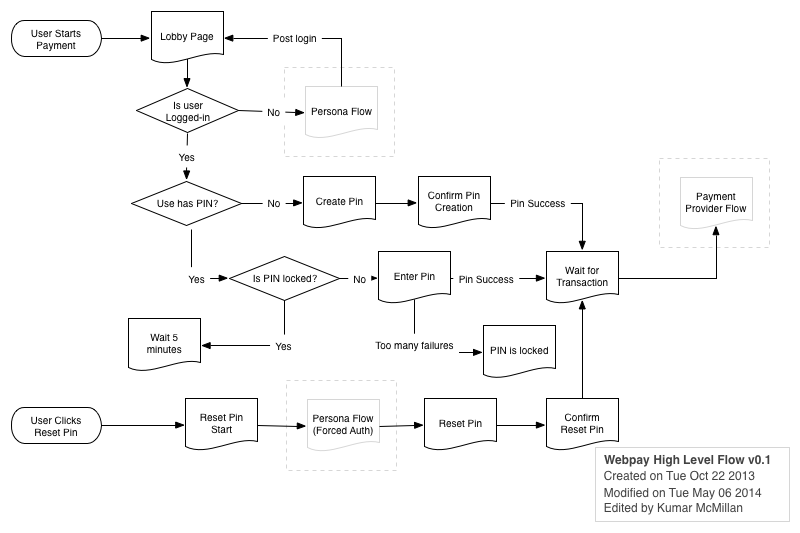
(Note: Persona was replaced with FxA)
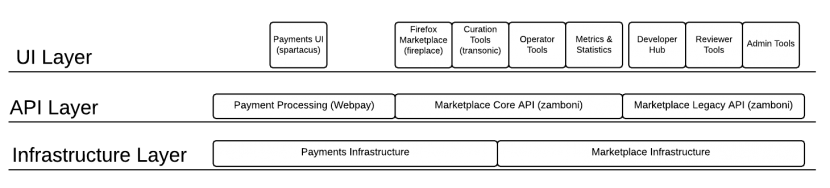
Architecture Diagram
Top-level architecural view
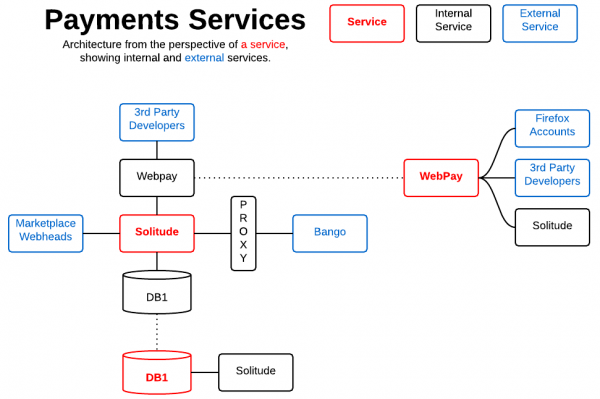
Payment Systems Diagram
Logical diagram of Payments application services architecture.
Diagram Key
The dotted line from a red service goes to a breakout describing the logical components of its service stack. This is a logical diagram, it does not represent the deployed physical network or server architecture.
Starting from a Red Services box,
- Solid line represents dependency/backend component relationships
- Dotted lines point to breakouts describing the logical components of a service stack
Mozilla Services
| Component Name | Description | Documentation URLs |
|---|---|---|
| DB1 | Example | Example |
| Solitude | A server for processing payments for Mozilla’s Marketplace and Add-ons site. | Project Documentation - http://readthedocs.org/docs/solitude/en/latest/ Sourcecode - https://github.com/mozilla/solitude |
| Webpay | Webpay is an implementation of the WebPaymentProvider spec Spartacus is a single page app front-end for Webpay. |
Webpay Sourcecode - https://github.com/mozilla/webpay Spartacus Sourcecode - https://github.com/mozilla/spartacus |
External Services
| Component Name | Description | Documentation URLs |
|---|---|---|
| 3rd Party Developers | Example | Example |
| Bango | Example | Example |
| Firefox Accounts | Example | Documentation - https://wiki.mozilla.org/Identity/Firefox_Accounts
|
| Marketplace Webheads | Example | Example |
| Proxy | Example | Example |
Stage 2: Design
Threat Model
| ID | Title | Threat | Proposed Mitigations | Threat Agent | Rating | Likelihood | Impact | Notes |
| 1 | malicious access to apps device | If a phone is stolen or given to a friend/family member, it is possible for that person to make purchases. | A PIN is to be implemented that is required for purchases and in-app purchases. CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal wiht stolen phone. | Malicious User | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | In other systems (i.e. iOS, this i a configured parameter. |
| 2 | Malicious extension could steal authentication credentials | A rogue extension could possibly steal credentials or cause transactions to happen. | A PIN is to be implemented that is required for purchases and in-app purchases. CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal with stolen credentials. | Malicious Developer | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | Must be registered with marketplace. |
| 3 | Malicious App creates fake iframe | An app could create an iframe in order to overlay a purchase iframe. | CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal with stolen credentials. | Malicious App | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 4 | Malicious App creates fake iframe | An app could create an iframe in order to overlay a purchase iframe. | CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal with stolen credentials. Paypal account shows all purchases. | Malicious App | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 5 | XSS vuln could allow malicious user to force purchase | If a XSS is found in the marketplace, this could be used to force a purchase. | CSP is enabled on Payments. CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal with stolen credentials. Paypal account shows all purchases. | Malicious App | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 6 | CSRF could force purchase. | If a XSS is found in the marketplace, this could be used to force a purchase. | CSRF protection token on the marketplace site. CEF logging on transactions to track excessive purchases. Incident response to deal with stolen credentials. | Malicious App | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 7 | Compromise web heads | The attacker could then leverage their access to attack other parts of the application environment or to serve arbitrary/manipulated content to users. | Mitigation possibilities are being discussed. | System access | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 8 | Appplication Theft | The attacker could begin a payment, cancel the payment, and craft a postback to the app server, fooling it into thinking the cancelled payment was successful. (BID 1145024) | Bug detected, application patched. | System access | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation | |
| 9 | Appplication Theft | The attacker could modify the JWT for payment to craft $0 payment that executes successfully. (BID 1145024) | Bug detected, application patched. | System access | 12 | 3 | 4 – Reputation |
User Interactions
Payment flow user interactions for
- Marketplace App Payment Flows
- In-App Payment Flows
Marketplace App Payment Flows
Payments flows are initiated from the Marketplace which is under Mozilla’s control
A. Desktop
| ID | Actions | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pre-provider flows PIN creation/enter/reset etc (Same domain as marketplace) | Popup |
| 2. | Provider payment entry | Popup, page hosted by payment provider |
| 3. | Communication with popup | Javascript library: fxpay |
B. Firefox OS / Android
| ID | Actions | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pre-provider flows PIN creation/enter/reset etc (Same domain as marketplace) | Trusted UI |
| 2. | Provider payment entry | Trusted UI, page hosted by payment provider |
| 3. | Open and communicate with Trusted UI | JavaScript platform function: navigator.mozPay() |
| 4. | Open and communicate with MozPay | JavaScript library: fxpay |
In-App Payment Flows
Payment flows are initiated from 3rd party app domains - Mozilla no control over the apps or domains. They have been approved by and have a payments account on the Marketplace, but can change their code at any time (for hosted apps).
A. Desktop
| ID | Actions | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pre-provider flows PIN creation/enter/reset etc (3rd party app domain) | Popup, page hosted by payment provider |
| 2. | Provider payment entry | Popup, page hosted by payment provider |
| 3. | Communication with popup | Javascript payments library run from 3rd party app domain: fxpay |
B. Firefox OS / Android
| ID | Actions | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pre-provider flows PIN creation/enter/reset etc (Same domain as marketplace) | Trusted UI |
| 2. | Provider payment entry | Trusted UI, page hosted by payment provider |
| 3. | Open and communicate with Trusted UI | JavaScript platform function: navigator.mozPay() |
| 4 | Open and communicate with MozPay | JavaScript library: fxpay |
Security Recommendations / Open Issues
| ID | Title | Status | Summary |
| [[1]] | Title | Status(Open/Closed) | Summary. |
| [[2]] | Title | Status(Open/Closed) | Summary. |
CEF Logging Requirements
Authentication
- bad password provided at login (or anywhere where user is prompted for auth)
- bad username provided at login
- account created
- password changed
- password reset requested
- new privileged (e.g. reviewer, admin, etc) account created
- account modified and granted additional rights (e.g. reviewer, admin, etc)
Authorization
Denial of Service
Request Specific
Input Validation Exceptions
File Upload
- Large number of file uploads
- Attempt to upload something other than expected file
Privacy Risk Analysis
(Status of and link to privacy review and outcome here)
Stage 3: Planning
Application Security Requirements
It is expected that the Secure Coding Guidelines is followed but these requirements are especially important for this application.
CSP Content Security Policy in blocking mode.
Password Requirements
- Threshold based CAPTCHA for login Restrict password guesses without CAPTCHA to 5.
- Blacklist top bad passwords that could be selected by a user.
Account Requirements
- Allow users to view last login time and IP address after authentication
Coding Requirements
- Session based CSRF protection (e.g. not Django cookie based CSRF protection)
- Clickjacking (x-frame-options) and XSS protection (CSP)
Other Requirements
- Uploaded links must be verified against google safe browsing list (real time or daily cron)
- Uploaded images must be strictly checked to validate only images are uploaded. More Info
SSL Requirements
- SSL is required to the connection to paypal (user redirects and any backend connections)
- The SSL cert must be strictly validated (specific code needed for backend connections)
- HSTS must be enabled
- No HTTP pages. Full HTTPS
- Third party connections (e.g. twitter, facebook, paypal, etc) must link to the HTTPS page for that site. That may require rewriting the widget (twitter specifically)
Operation Security Requirements
Document network/platform security requirements here (e.g. IDS concerns, firewall changes, system hardening reqs, etc)
Critical Security Requirements
Itemize individual security blockers here. Reference components in section AppSec or OpSec subsections. These blockers must be addressed before the product can go live.
Stage 4: Development
Repeatable Security Test Cases
Document individual repeatable security test cases here. Include a reference to the source repo, and documentation that governs how to execute test cases.
Secure Coding Guidelines
Document specific secure coding guidelines to be followed and relate them to specific issues/requirements that are specified; capture bug ids related to those issues.
Code Review Milestones
Table 1 - itemized list of code review milestones {i.e. breakdown of specific components that will be reviewed} Table 2 - list of app components/modules that should trigger additional security review (e.g. auth, csrf, file upload handling, etc)
Stage 5: Release
Application Security Verification
These subsections should contain a list of the steps to be taken, and the status of each activity
Code Review
Automated Security Testing
- Minion scanner
Manual Security Testing
Operational Security Verification
ArcSight Information
Network Design Security Review
Database Security Review
Platform Security (Hardening & Specific Config Requirements)
Landing Criteria
This should be a table itemizing everything from Stage 3 - Critical Security Requirements, including status. For status Red=Unimplemented,Yellow=implemented,Green=tested and passed?
Stage 6: Post Implementation Review
Production Security Considerations
Document additional/ongoing work for this application (e.g. specific things to watch for in ArcSight, gaming behaviour, etc)
Post Implementation Tasks
Itemize process/kb changes developed from this project (e.g. secure coding guidelines, policy stuff, etc)
Team status notes
| status | notes | |
|---|---|---|
| Products | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |
| Engineering | tbd | - |