B2G/Bluetooth-bluedroid
Contents
- 1 Switch Bluetooth stack bewteen bluez/bluedroid
- 2 b2g bluedroid branch
- 3 Enable bluedroid on flame (JB-based)
- 4 How does GeckoBluetooth choose to use bluez or bluedroid?
- 5 Bluetooth interfaces
- 6 GeckoBluetooth for bluedroid
- 7 Some notes about gonk-jb bluedroid stack:
- 8 Debugging:
- 9 Customize bluedroid stack
- 10 Gecko support
- 11 Porting
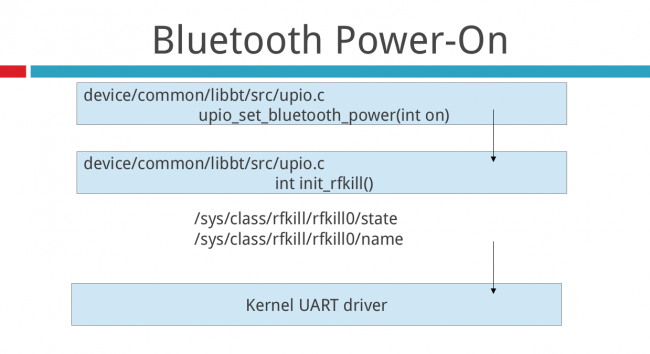
- 12 Power-on sequence
Switch Bluetooth stack bewteen bluez/bluedroid
For version JB 4.2, if you want to use bluez on JB, you need to modify some files.
See [Bug 911038][1]
b2g bluedroid branch
https://github.com/mozilla-b2g/platform_external_bluetooth_bluedroid
Enable bluedroid on flame (JB-based)
See: https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1004896
- Apply https://github.com/shuangMoz/b2g-manifest/commit/3d8d97a5d89366fd51a75755e4f8d045b41617fa into your .repo/manfiest.xml, this can make your gecko build choose to build bluedroid based
adb remount tar jxvf replace-bluez-flame.tar.bz and run replace_bluedroid_reply.sh when you connected with your device
- Apply patch replace-bluez-flame-gecko.patch and ./build.sh gecko && ./flash.sh gecko
Gecko bluetotoh will run bluedroid now.
### replace_bluedroid_reply.sh adb push audio.a2dp.default.so /system/lib/hw adb push bt_stack.conf /system/etc/bluetooth adb push bt_did.conf /system/etc/bluetooth adb push stack.conf /system/etc/bluetooth adb push auto_pair_devlist.conf /system/etc/bluetooth adb push libbt-utils.so /system/lib adb push libbt-hci.so /system/lib adb push bluetooth.default.so /system/lib/hw adb push bdt /system/bin ######## vendor ######### adb push libbt-vendor.so /system/vendor/lib
How does GeckoBluetooth choose to use bluez or bluedroid?
In configure.in, it checks whether folder path external/bluetooth/bluez or external/bluetooth/bluedroid exists.
Bluetooth interfaces
- bt_interface_t
- Bluedroid implemented as bluetoothInterface in external/bluetooth/bluedroid/btif/src/bluetooth.c: System control BT adapter.
- See: external/bluetooth/bluedroid/btif/src/bluetooth.c
- You need to use |get_bluetooth_interface()| to access all avaiable GAP profile functions.
- btav_interface_t
- Bluedroid implemented as bt_av_interface in external/bluetooth/bluedroid/btif/src/btif_av.c: System control A2DP service
- audio_hw_device and audio_stream_out: Bluedroid implemented in external/bluetooth/bluedroid/audio_a2dp_hw/audio_a2dp_hw.c: AudioFlinger uses A2DP client as audio output device.
- tHCI_IF: Bluedroid implemented as hci_h4_func_table in external/bluetooth/bluedroid/hci/src/hci_h4.c: Bluedroid HCI interface (data/cmd/evt in/out)
- bt_hc_interface_t: Bluedroid defined, Bluedroid implemented as bluetoothHCLibInterface in external/bluetooth/bluedroid/hci/src/bt_hci_bdroid.c:
Wrapper of tHCI_IF, has bt_hc_worker_thread to serialize downcoming HCI commands and read upcoming data/evt from HCI device.
- HFP, A2DP profile interfaces, you need to call |get_profile_interface()| to access profile interfaces.
See |hardware/libhardware/include/hardware| header files
GeckoBluetooth for bluedroid
- GAP: dom/bluetooth/bluedroid/gonk/BluetoothServiceBluedroid.cpp
- HFP/A2DP/OPP Profiles under: dom/bluetooth/bluedroid
See also bluedroid metabug for more information Bug 876583 [2]
Some notes about gonk-jb bluedroid stack:
What do we care about?
HAL API all exposed in hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/, bluetooth.h defines all BluetoothAdapter needed.
In general bluedroid apis are callback instead of dbus style programming.
GAP profile: external/bluetooth/bluedroid/btif/src/btif_dm.c
Important data structures: bt_property_t.
For "device found" callback, possible properties from device_found are:
properties[1]. type = BT_PROPERTY_BDNAME
properties[2]. type = BT_PROPERTY_BDADDR
properties[4]. type = BT_PROPERTY_CLASS_OF_DEVICE
properties[5]. type = BT_PROPERTY_TYPE_OF_DEVICE
properties[11]. type = BT_PROPERTY_REMOTE_RSSI
Adapter property maps to: sBluetoothInterface->get_adapter_property((bt_property_type_t) type) adapter_properties_callback
For adapter/remote device properties type, check btif/src/btif_storage.c, function cfg2prop.
Bluetooth Socket interface. bluedroid only provides two API, connect and listen. To receive connected or disconnected, you have to read connection signal. connection signal format as:
typedef struct {
short size;
bt_bdaddr_t bd_addr;
int channel;
int status;
} __attribute__((packed)) sock_connect_signal_t;
Debugging:
In /system/etc/bluetooth/bt_stack.conf defined logging level and logger output.
#Enable BtSnoop logging function #valid value : true, false BtSnoopLogOutput=true #BtSnoop log output file BtSnoopFileName=/sdcard/btsnoop_hci.log
In /system/etc/bluetooth/bt_stack.conf defined
logging level, this effected what we saw in logcat
You can use Wireshark or frontline viewer to open it.
Log level
#Trace level configuration #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_NONE 0 ( No trace messages to be generated ) #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_ERROR 1 ( Error condition trace messages ) #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_WARNING 2 ( Warning condition trace messages ) #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_API 3 ( API traces ) #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_EVENT 4 ( Debug messages for events ) #BT_TRACE_LEVEL_DEBUG 5 ( Full debug messages ) TRC_HCI=2 TRC_L2CAP=2 TRC_RFCOMM=2
Another way to enable external runtime parse tool such as hcidump is to enable BTSNOOP_EXT_PARSER_INCLUDED. See hci/include/bt_hci_bdroid.h, by default the debugging port is port 4330.
Turn off optimization Recomplile bluedroid stack with LOCAL_CFLAGS += -O0 (http://androidxref.com/4.3_r2.1/xref/external/bluetooth/bluedroid/main/Android.mk#116).
Log tool
Grab offline tool from [3]
- togglelog.sh: Enable/Disable bluedroid log
- openlog.sh: Download bluedroid log and use wireshark to check
Customize bluedroid stack
There is one bdroid_buildcfg.h file under device/vendor_name/device_name/bluetooth. This header file is for override configuration during build time. For example, BTM_DEF_LOCAL_NAME is for changing local adapter name.
Gecko support
See configure.in, it is to check whether folder external/bluetooth/bluez or external/bluetooth/bluedroid exists.
Porting
Nexus 4 Porting:
Make sure qct libbt-vendor had been compiled so you will see libbt-vendor.so in
the device.
Path is /system/vendor/lib/libbt-vendor.so
libbt-vendor source code is in: hardware/qcom/bt/libbt-vendor
You need to make sure the following .so files are in Nexus 4.
/system/lib/libbt-hci.so, libbt-utils.so
/system/lib/hw/audio.a2dp.default.so, bluetooth.default.so
/system/vendor/lib/libbt-vendor.so
To build bluedroid library for your device with b2g project, please add a config like this:
https://github.com/shuangMoz/device-mako/commit/58a9889b70f1c21b52386af8800d0e525cd4947c
For bcm chipset, source code in device/common/libbt
(Vendor specific folder) which generates
libbt-vendors.so.
device/common/libbt/include/vnd_machinename.txt , defines UART port and firmware patchram location.
**Note: BCM chipset vendor library location changes to platform/hardware/broadcom/libbt and under hardware/broadcom/libbt, in Android 4.4.
For Qct chipsets, power on Bluetooth chipset still depends on "/sytem/etc/init.qcom.bt.sh". See hardware/qcom/bt/libbt-vendor/src/hardware.c , function hw_config().
You need to also make sure /sytem/etc/init.qcom.bt.sh can be executed.
bluedroid config path:
/etc/bluetooth/bt_stack.conf
bluedroid storage path:
/etc/bluetooth/bt_did.conf
/etc/bluetooth/auto_pair_devlist.conf
All path stores in:
/data/misc/bluedroid
The format of bt_config.xml
/data/misc/bluedroid/bt_config.xml
Sample:
<N21 Tag="84:7a:88:fe:7e:f6">
<N1 Tag="Timestamp" Type="int">1372749957</N1>
<N2 Tag="Name" Type="string">unagi plus</N2>
<N3 Tag="DevClass" Type="int">5898764</N3>
<N4 Tag="DevType" Type="int">1</N4>
<N5 Tag="LinkKeyType" Type="int">5</N5>
<N6 Tag="PinLength" Type="int">0</N6>
<N7 Tag="LinkKey" Type="binary">a6a59a57c4effbcc432af4e2d21def9e</N7>
<N8 Tag="Service" Type="string">0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 00001105-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 00001116-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 0000112f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 00001112-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 00001132-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb 00006675-7475-7265-6469-616c62756d70 </N8>
</N21>
What remote_device_properties_callback returns records such as:
BD Name - Bluetooth Device Name Remote friendly name - User defined friendly name of the remote device Class - Bluetooth Class of Device as found in Assigned Numbers Type - Device Type - BREDR, BLE or DUAL Mode Bluetooth Service 128-bit UUIDs
Hardware configuration:
Take an example:
device/common/libbt/conf/samsung/maguro/bt_vendor.conf
# UART device port where Bluetooth controller is attached UartPort = /dev/ttyO1 # Firmware patch file location FwPatchFilePath = /vendor/firmware/